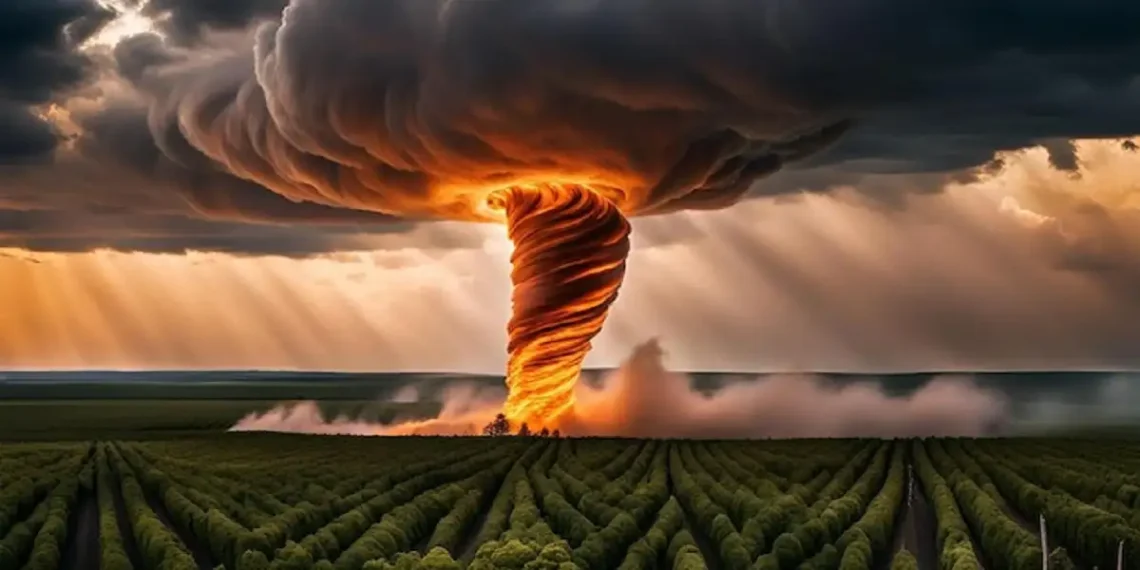
Fire fire:ybt0n0vvxu0= tornado, also known as fire whirls or fire devils, captivate the imagination with their mesmerizing and destructive power. These rare and extraordinary phenomena occur when intense heat and turbulent wind conditions combine to create a spinning vortex of fire. Unlike typical tornadoes, which consist of rotating columns of air, fire tornadoes incorporate flames, smoke, and debris, creating a spectacular and dangerous natural event.
The Formation of Fire Tornadoes
To understand how fire tornadoes form, one must first grasp the basics of fire behavior and atmospheric dynamics. A fire tornado requires several specific conditions to develop: an intense heat source, strong winds, and a vertical column of rising hot air. Wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and industrial fires often provide the necessary heat and fuel.
- Intense Heat Source: The primary driver of a fire tornado is an intense heat source, usually a large wildfire. The fire heats the surrounding air, causing it to rise rapidly.
- Strong Winds: Wind plays a crucial role in the formation of a fire tornado. Strong, gusty winds create a horizontal movement of air, which can interact with the rising hot air from the fire.
- Vertical Column of Rising Air: The rising hot air creates a low-pressure area at the surface. As the hot air ascends, cooler air rushes in to replace it. This process can create a rotating column of air, similar to the formation of a regular tornado.
When these conditions align, the interaction between the rising hot air and the strong winds can cause the air to spin, forming a vortex. This vortex, filled with flames, smoke, and debris, becomes a fire tornado.
The Anatomy of a Fire Tornado
Fire fire:ybt0n0vvxu0= tornado vary in size and intensity, depending on the conditions that create them. They typically range from a few feet to several hundred feet in height and can have a diameter of a few feet to over 100 feet. The core of a fire tornado consists of intensely hot air, which can reach temperatures of over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit (1,093 degrees Celsius).
The outer layer of the fire tornado includes flames, burning debris, and smoke. This layer gives the fire tornado its distinctive fiery appearance. The rotating motion of the fire tornado can lift burning embers and debris into the air, spreading the fire and causing additional damage.
Notable Fire Tornado Events
Fire tornadoes, while rare, have occurred in various parts of the world, often during large wildfires. Some notable fire tornado events include:
- The Great Chicago Fire (1871): This infamous firestorm reportedly produced fire whirls that contributed to the rapid spread of the blaze, causing significant destruction.
- The Carr Fire (2018): In California, the Carr Fire generated a massive fire tornado with winds estimated at 143 miles per hour (230 kilometers per hour). This fire tornado caused extensive damage and claimed the lives of several people.
- The Black Saturday Bushfires (2009): In Victoria, Australia, the Black Saturday bushfires created fire whirls that contributed to the devastation of several communities. The intense heat and wind conditions led to the formation of multiple fire tornadoes.
The Dangers of Fire Tornadoes
Fire fire:ybt0n0vvxu0= tornado pose significant dangers due to their extreme heat, high winds, and the ability to spread flames over large distances. The intense heat within a fire tornado can ignite structures and vegetation, causing fires to spread rapidly. The high winds can lift and hurl burning debris, creating secondary fires and increasing the overall destruction.
Firefighters face immense challenges when dealing with fire tornadoes. The unpredictable nature of these phenomena makes them difficult to combat. Traditional firefighting techniques, such as creating firebreaks and using water or fire retardants, may prove ineffective against the intense heat and winds of a fire tornado.
Scientific Studies and Research
Researchers continue to study fire tornadoes to better understand their formation and behavior. Advanced technology, including high-speed cameras and weather modeling software, allows scientists to simulate and analyze fire tornadoes in controlled environments. These studies aim to improve fire prediction models and develop more effective firefighting strategies.
For example, researchers at the University of California, Riverside, have conducted experiments to recreate fire tornadoes in the lab. By manipulating heat sources and wind conditions, they have gained valuable insights into the dynamics of these fiery vortices. Their findings contribute to the development of predictive models that can help firefighters anticipate and respond to fire tornadoes more effectively.
Safety Measures and Preparedness
While fire tornadoes remain rare, individuals living in fire-prone areas should take precautions to protect themselves and their property. Here are some safety measures and preparedness tips:
- Create Defensible Space: Clear vegetation and flammable materials around your home to create a defensible space. This space can slow the spread of fires and provide a buffer zone for firefighters.
- Install Fire-Resistant Materials: Use fire-resistant building materials for roofs, siding, and decks. These materials can help protect your home from flying embers and intense heat.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and fire warnings from local authorities. Stay informed about fire conditions in your area and be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Create a family evacuation plan and practice it regularly. Identify multiple escape routes and designate a meeting point in case you become separated.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble an emergency kit with essential items such as water, non-perishable food, medications, and important documents. Keep this kit in a readily accessible location.
Conclusion
Fire fire:ybt0n0vvxu0= tornado, with their awe-inspiring yet destructive power, serve as a reminder of nature’s unpredictable and formidable force. Understanding the conditions that lead to their formation and the dangers they pose can help individuals and communities better prepare for and respond to these rare phenomena. As scientific research continues to advance, we can hope to gain more insights into fire tornadoes, ultimately improving our ability to predict and mitigate their impact. In the meantime, awareness and preparedness remain our best defense against the fiery whirlwinds of nature. See more